As topologias mais populares de conversor buck e boost dc / dc têm uma limitação significativa: a topologia buck pode apenas diminuir a tensão de entrada e a topologia boost apenas a aumenta. No entanto, existem tarefas em que a faixa de tensão de entrada requer operação simultânea para aumentar e diminuir, por exemplo, temos uma entrada de 3 ... 15V e na saída é necessário obter 12V estabilizados. Situação familiar?
Existem 2 soluções possíveis:
- Usando o conversor de reforço, aumente a tensão de entrada de 3 ... 15V para 15V estável na saída e, em seguida, usando a topologia buck, diminua a tensão para os 12V necessários;
- Aplique uma topologia de aumento de buck que resolva esse problema de maneira ideal.
A desvantagem óbvia do primeiro método é a necessidade de usar 2 bobinas, um número maior de capacitores e não o modo de operação mais ideal, o que significa menor eficiência. A topologia de reforço de cotovelo é desprovida dessas desvantagens, então hoje falaremos sobre isso. Para ser interessante, decidi não usar nenhum controlador pronto e implementei um conversor dc / dc controlado digitalmente com base no STM32F334C8T6.
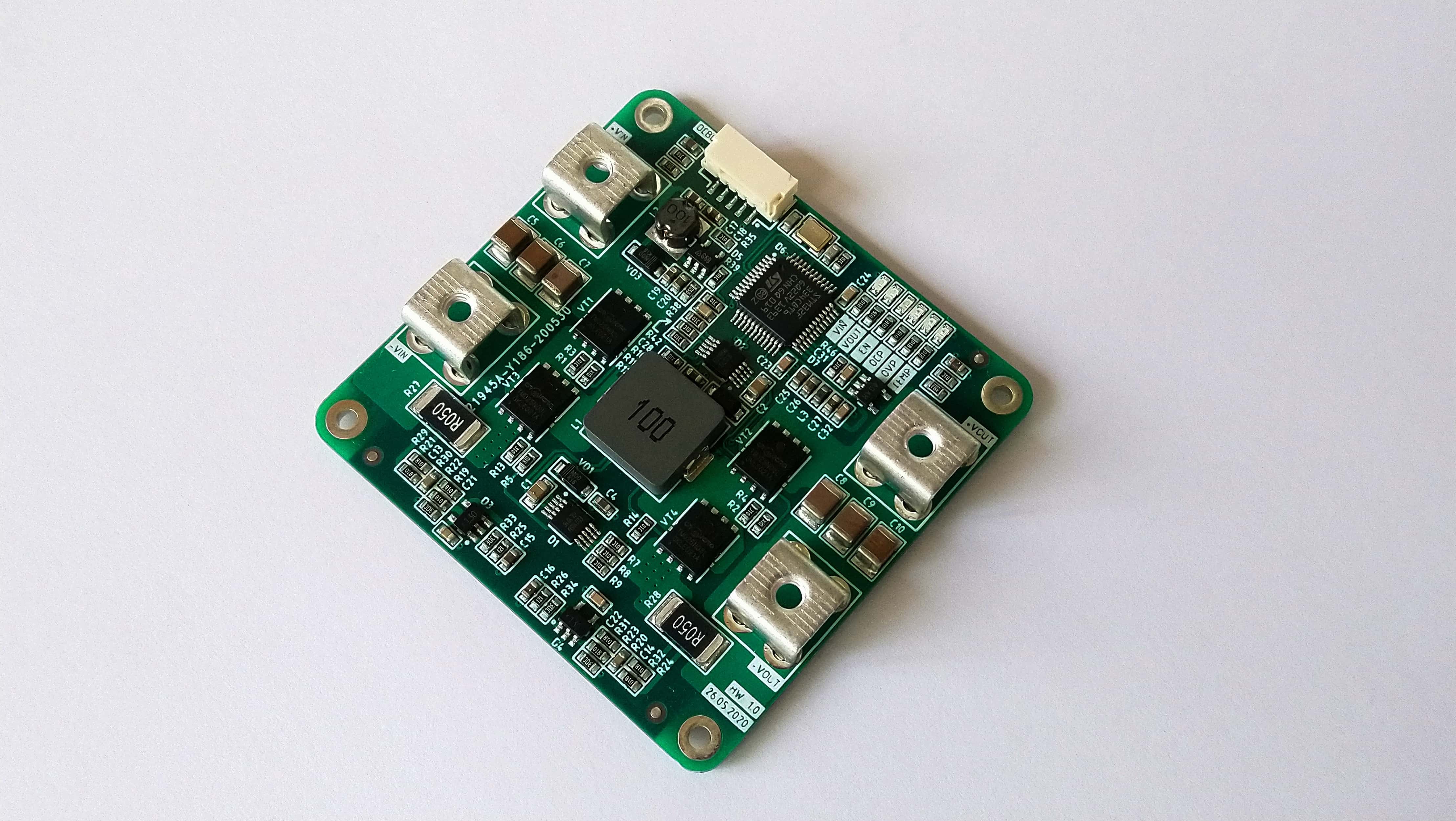
Dentro da estrutura deste artigo, falarei brevemente sobre a implementação de hardware do conversor e como implementar um sistema de controle para vários modos de operação. Interessante? Então vamos ...
1. Brevemente sobre a operação da topologia buck-boost
: 2 2 , .. , 2 (4 ). , . :
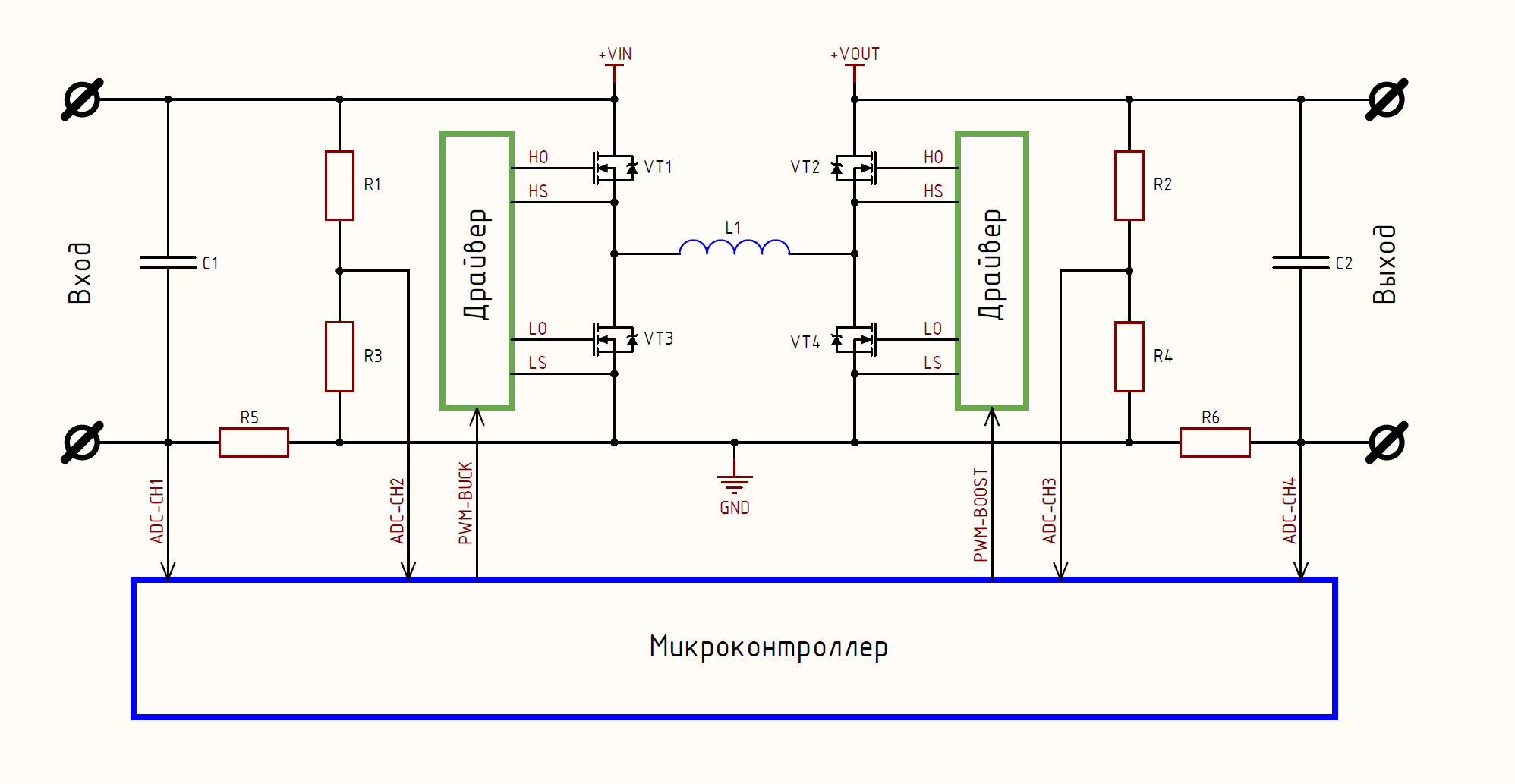
, : 2 ( 2 , ), 4 , . 1 2 (OCP) . 2 ? , , .
, , , STM32F334, STM32G474, XMC4108, TMS320F28027 , .. : HRPWM, , , . , , , . , , , (OCP) , , .
… buck-boost :

buck () boost (), — 3 buck-, L1C3 LC-. 3 boost-, . , buck-, boost-. .
buck:
boost:
, buck- boost :
buck-boost 3- : ( PWM-BUCK PWM-BOOST). , .
, . , 8, Dboost 70%, Dbuck 50%. :
, 8 . , , , 2 - :

. (duty) 2- . duty, .
2. .
2 , : . , , CC/CV . :

CC CV , : REF , , ; , , , , .
-, , " " . "" (REF), , , 10. , buck-boost , (duty). - . , .
:
O que isso nos dá? E agora sabemos quanto o valor real da tensão de saída se desvia do valor ajustado ( REF ). Isso nos permite entender se é necessário "dar um comando" para aumentar ou diminuir a tensão. Por exemplo, na topologia do fanfarrão , para aumentar a tensão, é necessário aumentar o dever do transistor superior e, para diminuir a tensão, reduzir o preenchimento adequadamente. Para a topologia do impulso , pelo contrário, e para o aumento do buck há 2 sinais, e aqui já é mais difícil - você precisa equilibrar, mas acho que, em média, a ideia é clara, para maior clareza, darei um pseudo-código para controlar o buck :
// -
uint16_t dutyPWM = 0;
// ,
const float referenceOutputVoltage = 10.0f;
// , , 1
void sTim3::handler (void) {
float outputVoltage = GetOutputVoltage();
if (outputVoltage > referenceOutputVoltage) {
dutyPWM--;
} else {
dutyPWM++;
}
}, . - ( ), , -, -:
// -
uint16_t dutyPWM = 0;
// ,
const float referenceOutputVoltage = 10.0f;
//
const float Kp = 1.0f;
// , , 1
void sTim3::handler (void) {
float outputVoltage = GetOutputVoltage();
float error = referenceOutputVoltage - outputVoltage;
dutyPWM += Kp * error;
}… , , (dutyPWM) buck , , . , (reference), dutyPWM .
, 1 , . error -. , dutyPWM .
buck dc/dc , 20. dutyPWM 0, 1000, buck Vout = Vin x dutyPWM = 20V x 0 = 0V, 0. ( №1) error = 10 — 0 = 10 dutyPWM = 10, Vout = Vin x dutyPWM = 20V x (10/1000) = 0.2V. 1 ( №2) error = 10 — 0.2V = 9.8V, dutyPWM = 19.8, (reference). , reference 10 ( ).
Kp, , . 1, . , 0.2 . () , , . Kp 10 : dutyPWM = Kp x error = 10 x (10 — 0) = 100, 0.2, Vout = Vin x dutyPWM = 20V x (100/1000) = 2V, " " 10 . Kp . , , , , .
… ? , .
3. CV mode
CV mode, . ( ), , , : - ++. , . , .
STM32F334C8T6, , HRPWM . , , . , (2-3-4) , , .
CV :
/***********************************************************
* 200 ,
* HRPWM - 30 000.
* : 3...15
* : 20
*
* : 12
***********************************************************/
void sTim3::handler (void) {
TIM3->SR &= ~TIM_SR_UIF;
float inputVoltage = Feedback::GetInputVoltage();
// boost, Vin < 90% * Vref
if (inputVoltage <= (Application::referenceOutputVoltage * 0.9)) {
Hrpwm::SetDuty(Hrpwm::Channel::buck, 29000);
float outputVoltage = Feedback::GetOutputVoltage();
pidVoltageMode
.SetReference(Application::referenceOutputVoltage)
.SetSaturation(-29800, 29800)
.SetFeedback(outputVoltage, 0.001)
.SetCoefficient(10,0,0,0,0)
.Compute();
Application::dutyBoost += pidVoltageMode.Get()
Hrpwm::SetDuty(Hrpwm::Channel::boost, Application::dutyBoost);
}
// buck, Vin > Vref * 110%
if (inputVoltage >= (Application::referenceOutputVoltage * 1.1)) {
Hrpwm::SetDuty(Hrpwm::Channel::boost, 1000);
float outputVoltage = Feedback::GetOutputVoltage();
pidVoltageMode
.SetReference(Application::referenceOutputVoltage)
.SetSaturation(-29800, 29800)
.SetFeedback(outputVoltage, 0.001)
.SetCoefficient(10,0,0,0,0)
.Compute();
Application::dutyBuck += pidVoltageMode.Get()
Hrpwm::SetDuty(Hrpwm::Channel::buck, Application::dutyBuck);
}
// buck-boost, (90% * Vref) < Vin < (110% * Vref)
if ((inputVoltage > (Application::referenceOutputVoltage * 0.9)) && (inputVoltage < (Application::referenceOutputVoltage * 1.1))) {
Hrpwm::SetDuty(Hrpwm::Channel::boost, 6000);
float outputVoltage = Feedback::GetOutputVoltage();
pidVoltageMode
.SetReference(Application::referenceOutputVoltage)
.SetSaturation(-29800, 29800)
.SetFeedback(outputVoltage, 0.001)
.SetCoefficient(10,0,0,0,0)
.Compute();
Application::dutyBuck += pidVoltageMode.Get()
Hrpwm::SetDuty(Hrpwm::Channel::buck, Application::dutyBuck);
}
}… buck-boost, , 2- buck boost . 2- : . , , , .
/***********************************************************
* 200 ,
* HRPWM - 30 000.
* : 3...15
* : 20
*
* : 12
***********************************************************/
void sTim3::handler (void) {
TIM3->SR &= ~TIM_SR_UIF;
// boost
float inputVoltage = Feedback::GetInputVoltage();
if (inputVoltage < 6.0f) { Application::dutyBoost = 25000; }
if ((inputVoltage >= 6.0f) && (inputVoltage < 12.0f)) { Application::dutyBoost = 18000; }
if (inputVoltage >= 12.0f) { Application::dutyBoost = 6000; }
Hrpwm::SetDuty(Hrpwm::Channel::boost, Application::dutyBoost);
// buck
float outputVoltage = Feedback::GetOutputVoltage();
pidVoltageMode
.SetReference(Application::referenceOutputVoltage)
.SetSaturation(-29800, 29800)
.SetFeedback(outputVoltage, 0.001)
.SetCoefficient(10,0,0,0,0)
.Compute();
Application::dutyBuck += pidVoltageMode.Get();
Hrpwm::SetDuty(Hrpwm::Channel::buck, Application::dutyBuck);
}3 : 3...6, 6...12 12...15 boost , buck. , — , . , ( ), .
3 , , , , . dutyBoost : , buck boost-, 90% ( ). , 3...15 . dutyBoost — 3 15, , .. . dutyBuck 90% 3 "" boost- 3 x 0,9 = 2,7, boost 15 2.7! dutyBoost 1 — (Vout / Vin) = 1 — 2,7 / 15 = 82%, , - 30000, 30 000 x 82% = 24 600, 25000.
3, 5, buck 3. , dutyBoost, buck 90% 12. , ~3,2% . ? , , "" .
6...12 60% 18000, 12...15 20% 6000. - ...
3- . , , buck 100% boost-, boost dc/dc . , , — boost- 0% buckDuty, buck dc/dc . — , buck, boost buck-boost...
boost , "" 90% , Vref x 90% = 12 x 0,9 = 10,8. dutyBoost = 1 — (Vref x 90%) / (Vref x 110%) = 1 — 0,9 / 1,1 = 19% = 5700, 6000 . buck- buckDuty. "" buck-boost , . , :
4. CC mode
, . , , , LED, - , . , dc/dc , .. (duty), ?
— : U = I x R. , , , 10 . dc/dc 10 , I = U / R = 1, , .. . Li-ion , , 15, - 5, . , , I = U / R = const.
, , , . , , , I = U / R = const.
, 1. 1 1: I = 1 = const = U / R = 1 / 1 . 5 , 5: I = 1 = const = U / R = 5 / 5 . 5, 1 0.2 .
, , (error) , (dutyPWM). :
/***********************************************************
* 200 ,
* HRPWM - 30 000.
* : 3...15
* : 20
*
* : 1
***********************************************************/
void sTim3::handler (void) {
TIM3->SR &= ~TIM_SR_UIF;
float inputVoltage = Feedback::GetInputVoltage();
// boost, Vin < 90% * Vref
if (inputVoltage <= (Application::referenceOutputVoltage * 0.9)) {
Hrpwm::SetDuty(Hrpwm::Channel::buck, 29000);
float outputCurrent = Feedback::GetOutputCurrent();
pidCurrentMode
.SetReference(Application::referenceOutputCurrent)
.SetSaturation(-29800, 29800)
.SetFeedback(outputCurrent, 0.001)
.SetCoefficient(10,0,0,0,0)
.Compute();
Application::dutyBoost += pidCurrentMode.Get()
Hrpwm::SetDuty(Hrpwm::Channel::boost, Application::dutyBoost);
}
// buck, Vin > Vref * 110%
if (inputVoltage >= (Application::referenceOutputVoltage * 1.1)) {
Hrpwm::SetDuty(Hrpwm::Channel::boost, 1000);
float outputCurrent = Feedback::GetOutputCurrent();
pidCurrentMode
.SetReference(Application::referenceOutputCurrent)
.SetSaturation(-29800, 29800)
.SetFeedback(outputCurrent, 0.001)
.SetCoefficient(10,0,0,0,0)
.Compute();
Application::dutyBuck += pidCurrentMode.Get()
Hrpwm::SetDuty(Hrpwm::Channel::buck, Application::dutyBuck);
}
// buck-boost, (90% * Vref) < Vin < (110% * Vref)
if ((inputVoltage > (Application::referenceOutputVoltage * 0.9)) && (inputVoltage < (Application::referenceOutputVoltage * 1.1))) {
Hrpwm::SetDuty(Hrpwm::Channel::boost, 6000);
float outputCurrent = Feedback::GetOutputCurrent();
pidCurrentMode
.SetReference(Application::referenceOutputCurrent)
.SetSaturation(-29800, 29800)
.SetFeedback(outputCurrent, 0.001)
.SetCoefficient(10,0,0,0,0)
.Compute();
Application::dutyBuck += pidCurrentMode.Get()
Hrpwm::SetDuty(Hrpwm::Channel::buck, Application::dutyBuck);
}
}
, buck-boost . , (outputCurrent) - (referenceOutputCurrent) , , . :
, CV mode. - , 2 : , , , .
LED 10 1, :
5. CC/CV mode
, … :
- 10 Li-ion , , . , , ( ) , .
- 1, Li-ion , . … ? , , , , , — .
- , ? CC/CV, . : 1 Li-ion 4.2 , CC/CV 3...15 1. , 1 , CC , . , 15, CV, 15 ( ).
2 , .. , 15 , , 1 — , . 3, , , CV , . , :
/***********************************************************
* 200 ,
* HRPWM - 30 000.
* : 3...15
* : 20
*
* : 10 1
***********************************************************/
void sTim3::handler (void) {
TIM3->SR &= ~TIM_SR_UIF;
float resultPID = 0.0f;
float inputVoltage = Feedback::GetInputVoltage();
// boost, Vin < 90% * Vref
if (inputVoltage <= (Application::referenceOutputVoltage * 0.9)) {
Hrpwm::SetDuty(Hrpwm::Channel::buck, 29000);
float outputVoltage = Feedback::GetOutputVoltage();
float outputCurrent = Feedback::GetOutputCurrent();
// CC mode, Vout < Vref
if (outputVoltage < (Application::referenceOutputVoltage - 0.2f)) {
pidCurrentMode
.SetReference(Application::referenceOutputCurrent)
.SetSaturation(-29800, 29800)
.SetFeedback(outputCurrent, 0.001)
.SetCoefficient(20,0,0,0,0)
.Compute();
resultPID = pidCurrentMode.Get();
}
// CV mode, (Iout -> 0) (Vout => Vref)
if ((outputCurrent < 0.05f) || (outputVoltage >= (Application::referenceOutputVoltage - 0.2f))) {
pidVoltageMode
.SetReference(Application::referenceOutputVoltage)
.SetSaturation(-29800, 29800)
.SetFeedback(outputVoltage, 0.001)
.SetCoefficient(50,0,0,0,0)
.Compute();
resultPID = pidVoltageMode.Get();
}
Application::dutyBoost += resultPID;
Hrpwm::SetDuty(Hrpwm::Channel::boost, Application::dutyBoost);
}
// buck, Vin > Vref * 110%
if (inputVoltage >= (Application::referenceOutputVoltage * 1.1)) {
Hrpwm::SetDuty(Hrpwm::Channel::boost, 1000);
float outputVoltage = Feedback::GetOutputVoltage();
float outputCurrent = Feedback::GetOutputCurrent();
// CC mode, Vout < Vref
if (outputVoltage < (Application::referenceOutputVoltage - 0.2f)) {
pidCurrentMode
.SetReference(Application::referenceOutputCurrent)
.SetSaturation(-29800, 29800)
.SetFeedback(outputCurrent, 0.001)
.SetCoefficient(20,0,0,0,0)
.Compute();
resultPID = pidCurrentMode.Get();
}
// CV mode, (Iout -> 0) (Vout => Vref)
if ((outputCurrent < 0.05f) || (outputVoltage >= (Application::referenceOutputVoltage - 0.2f))) {
pidVoltageMode
.SetReference(Application::referenceOutputVoltage)
.SetSaturation(-29800, 29800)
.SetFeedback(outputVoltage, 0.001)
.SetCoefficient(50,0,0,0,0)
.Compute();
resultPID = pidVoltageMode.Get();
}
Application::dutyBuck += resultPID;
Hrpwm::SetDuty(Hrpwm::Channel::buck, Application::dutyBuck);
}
// buck-boost, (90% * Vref) < Vin < (110% * Vref)
if ((inputVoltage > (Application::referenceOutputVoltage * 0.9)) && (inputVoltage < (Application::referenceOutputVoltage * 1.1))) {
Hrpwm::SetDuty(Hrpwm::Channel::boost, 6000);
float outputVoltage = Feedback::GetOutputVoltage();
float outputCurrent = Feedback::GetOutputCurrent();
// CC mode, Vout < Vref
if (outputVoltage < (Application::referenceOutputVoltage - 0.2f)) {
pidCurrentMode
.SetReference(Application::referenceOutputCurrent)
.SetSaturation(-29800, 29800)
.SetFeedback(outputCurrent, 0.001)
.SetCoefficient(20,0,0,0,0)
.Compute();
resultPID = pidCurrentMode.Get();
}
// CV mode, (Iout -> 0) (Vout => Vref)
if ((outputCurrent < 0.05f) || (outputVoltage >= (Application::referenceOutputVoltage - 0.2f))) {
pidVoltageMode
.SetReference(Application::referenceOutputVoltage)
.SetSaturation(-29800, 29800)
.SetFeedback(outputVoltage, 0.001)
.SetCoefficient(50,0,0,0,0)
.Compute();
resultPID = pidVoltageMode.Get();
}
Application::dutyBuck += resultPID;
Hrpwm::SetDuty(Hrpwm::Channel::buck, Application::dutyBuck);
}
}
, , if, . .
, 2 -, , — -. CC mode CV mode. : (Application::referenceOutputVoltage) , CV mode, 15. , CC mode 1.
, / , . , LED 2 . , , 10 STM32F334 .
buck-boost dc/dc CC/CV:
...
lamerok veydlin, (, , ), !
, : https://t.me/proHardware. , , , , , .
, . buck-boost-, , , - , .